MARVEL researchers introduce a novel heat transport theory in quest for more efficient thermoelectrics
by Carey Sargent, EPFL, NCCR MARVEL
Crystals and glasses conduct heat in fundamentally different ways: the regular arrangement of atoms in a crystal means that heat is conducted by the propagation of vibrational waves – this is what happens, for instance, in a silicon chip inside your computer.
In glasses, which are disordered down to the atomic scale, heat is transferred much more slowly by a random hopping of vibrations. In 1929, the physicist Rudolf Peierls laid the foundations for describing heat transfer, applying to crystals the still recent transport theory of Boltzmann, and deriving the celebrated transport equation for phonons—it has been the stalwart of microscopic theories of heat transfer ever since.
After many decades, and helped by the rapidly developing field of molecular dynamics simulations, Philip Allen and Joseph Feldman followed up in 1989 with an equation applicable to glasses. Now, MARVEL scientists have figured out how to derive a more general formulation that describes equally well both classes of materials, as well as everything in between.
In the paper Unified theory of thermal transport in crystals and glasses, out now in Nature Physics, EPFL PhD student Michele Simoncelli, together with Nicola Marzari, director of NCCR MARVEL, and a professor in the Institute of Materials, and Professor Francesco Mauri at the University of Rome La Sapienza derive from a general theory for dissipative quantum systems the microscopic equation that takes into account both the particle-like and the wave-like characteristics of heat transfer.
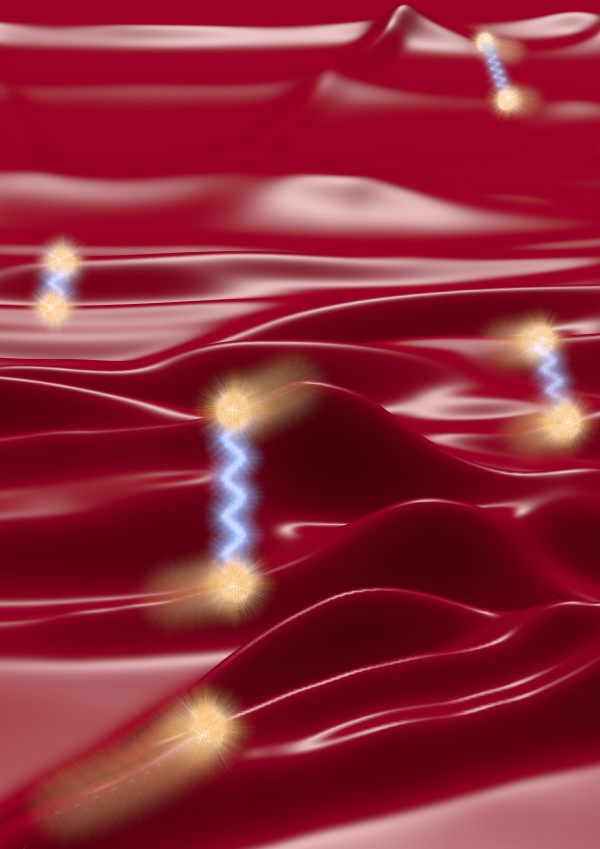
Heat conduction originates from both particle-like diffusion of phonon wave-packets (blurred spheres, following the realistic 3D phonon dispersion of CsPbBr3) and wave-like tunneling (blue waves).
Tunneling emerges when the spacings between phonon branches (Lorentzian-shaped ridges, whose heights quantify the heat carried) become comparable to their line-widths (proportional to the widths of the ridges).
Image credit: Michele Simoncelli, EPFL
It turns out that Peierls had discarded a key component in heat propagation, where vibrational excitations can tunnel, quantum-like, from one state to another. While such tunneling contributions are negligible in perfect crystals, they become more and more relevant as a system becomes disordered, and in a glass they give rise to the Allen-Feldman formalism. But the new equation is much more general and can be applied with equal accuracy to any material, encompassing the emergence and coexistence of all known vibrational excitations. Critically, this new theory of heat conduction covers the materials that are both crystal-like and glass-like: these have major technological importance, because they can be very good thermoelectrics, that is, materials that can convert heat into electricity, or electricity into cooling.
Thermoelectric materials could be tremendously important in energy applications because they generate electricity from available or “waste” heat such as that coming from our industrial processes, car and truck engines, or simply from the sun. Having thermoelectric materials that are more efficient (around three times the current standard) would change all our refrigeration and air-conditioning technologies completely because thermoelectric materials can be used in reverse and exploit electricity to cool us down, rather than producing electricity out of heat. (And if you think that studying refrigerators is distinctively uncool (pun intended), it’s worth remembering that Albert Einstein worked on refrigerators for 8 years, from 1926 to 1934, and at the height of his intellectual powers, together with his student Leó Szilárd – he even patented a refrigerator with no moving parts, as would happen in a thermoelectric fridge).
Creating such devices however requires a thorough understanding of how and to what extent heat conducts. And until now, theory and modelling has had limited success. A good thermoelectric needs to be an electrical conductor, and thus quite crystalline, but also a thermal insulator, and thus quite glassy—it needs to be able to carry and condense positive and negative charges on two different sides of a device, creating an electrical potential. Trying to treat thermoelectrics as either crystals or glasses in terms of the heat transport equations available until now however would result in very large errors and so it has been very difficult to predict their efficiency.
The new understanding outlined in the paper and more accurate estimates of thermal conductivity, along with data on the electrical conductivity, will allow scientists to calculate the “figure of merit” of thermoelectrics, and provide an estimate of their efficiency. Armed with this key piece of information, researchers will be able to screen potential materials first with computational techniques, accelerating the development path for these new technologies.
Reference: Unified theory of thermal transport in crystals and glasses,
Michele Simoncelli(1), Nicola Marzari(1), and Francesco Mauri(2)
(1) Theory and Simulation of Materials (THEOS) and National Centre for Computational Design and Discovery of Novel Materials (MARVEL), École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland. (2) Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Roma La Sapienza, Piazzale Aldo Moro 5,
I-00185 Roma, Italy.
Low-volume newsletters, targeted to the scientific and industrial communities.
Subscribe to our newsletter